How to Treat Hereditary Baldness and Regrow Hair
|
Reading time: 13 minutes
|

Key Takeaways
- Hereditary baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, affects about 66% of men by age 35. It often shows up as thinning hair or a receding hairline. A hormone called DHT (dihydrotestosterone) is a key factor. DHT causes hair follicles to weaken, leading to thinner hair over time and eventually stopping hair growth completely.
- Modern treatments can help slow or even reverse hair loss. Options include:
-
- Finasteride (Propecia): A daily pill that reduces DHT levels.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that improves blood flow to the scalp, promoting hair regrowth.
- Ketoconazole Shampoo: Helps reduce DHT on the scalp and supports other treatments.
For advanced cases, surgical options like follicular unit extraction (FUE) can provide long-term results. Combining these treatments often gives the best outcomes.
- Picking the best treatment depends on factors like:
-
- Cost: Medications are affordable, but surgeries like FUE are more expensive.
- Severity of Hair Loss: Use tools like the Norwood scale to assess how much hair loss you have.
- Personal Preferences: Consider what fits your routine and goals, like medications for convenience or surgery for a permanent solution.
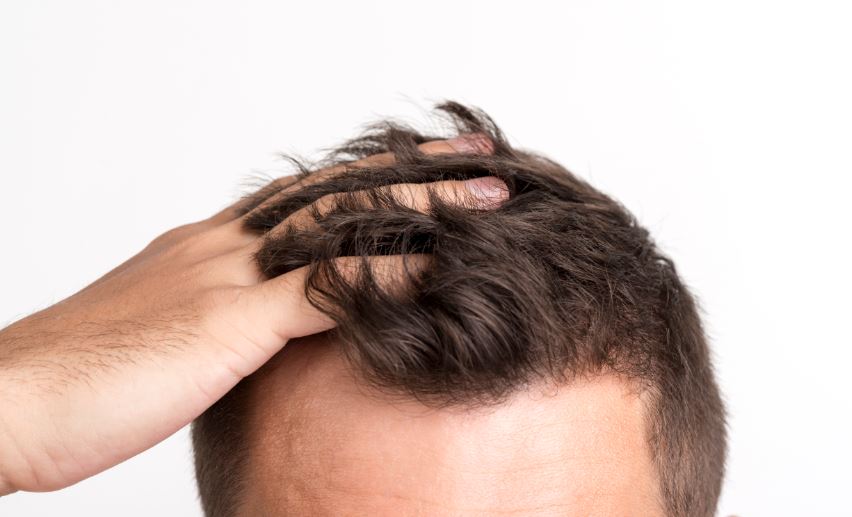
Hereditary baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a condition that affects millions of men around the world. By the age of 35, about 66% of men notice some form of hair loss. This condition is strongly linked to genetics, meaning that men with bald relatives are more likely to experience it themselves.
Advances in medical science and technology have made it possible to understand the causes of hereditary baldness and explore effective treatment options. These solutions range from medications that slow or stop hair loss to procedures that restore hair. This guide will explain what hereditary baldness is, how it progresses, and the treatments available to help manage it.
What Is Hereditary Baldness?
Hereditary baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, is the most common reason men lose their hair. This condition is passed down through family genetics. If a man has bald relatives, like his father, uncles, or brothers, he is more likely to experience hair loss too. While the exact way it is inherited can differ, a family history of baldness is a strong clue.
The progression of hereditary baldness varies between individuals. Some men notice their hair thinning gradually across the top of their head while keeping the overall shape of their hairline. Others may see their hairline begin to recede, often forming a horseshoe-shaped pattern over time. These changes usually happen slowly, making it hard to predict exactly how much hair will be lost or how quickly it will happen.
A hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a big role in hereditary baldness. DHT is made from testosterone, a hormone found in all men. However, some men are more sensitive to DHT. When DHT attaches to hair follicles, it causes them to shrink and weaken. This makes the hair in those follicles grow thinner and shorter until the follicles stop producing hair altogether.
To understand and measure how much hair has been lost, doctors use the Norwood scale. This tool classifies hair loss from Stage 1, which means little to no hair loss, to Stage 7, where most of the hair is gone except for the sides and back of the head. The Norwood scale helps doctors decide the best treatment options based on the severity of hair loss.
Effective Treatment Options for Hereditary Baldness
Hereditary baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, can now be managed with modern treatments. These options help slow, stop, or even reverse hair loss. Different treatments target different causes of hair loss, giving men the ability to choose the best solution for their needs.
Finasteride as a Top Medical Treatment
Finasteride, sold under the brand name Propecia, is one of the most effective treatments for hereditary baldness. This daily pill works by lowering levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that causes hair follicles to shrink and weaken.
By reducing DHT, finasteride protects hair follicles from further damage. Although it cannot revive follicles that are no longer active, it can stop hair loss in most men and even encourage moderate regrowth in many cases. This makes finasteride a reliable choice for managing hair loss.
Minoxidil and Its Role in Hair Regrowth
Minoxidil, sold as Rogaine, is another popular treatment for hereditary baldness. This is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp, usually twice a day. It comes in liquid or foam forms and works best on thinning areas.
Minoxidil improves blood flow to the scalp, which helps damaged hair follicles receive more nutrients. This increased circulation can promote hair growth, especially in areas where follicles are weak but still active. Many men use minoxidil along with finasteride for better results, as the two treatments address hair loss in different ways.
Ketoconazole Shampoo for Scalp Health
Ketoconazole shampoo, sold under the brand name Nizoral often used to treat dandruff, also benefits men with hereditary baldness. It reduces DHT levels on the scalp, which may slow down hair loss.
While ketoconazole is not usually effective on its own, it works well when combined with finasteride and minoxidil. This trio of treatments is commonly called “The Big Three” because they provide a strong, multi-faceted approach to managing baldness. Washing your hair with ketoconazole shampoo two to three times a week can support overall scalp health and improve the effectiveness of other treatments.
Hair Transplantation as a Surgical Option
For men with advanced hair loss, hair transplantation can be the most effective option. This procedure moves healthy hair follicles from the sides or back of the head—areas typically unaffected by baldness—to thinning or balding areas.
The most advanced method, called follicular unit extraction (FUE), involves transplanting individual follicles for a natural look with minimal scarring. This technique has replaced older methods, like follicular unit transplantation (FUT), which often left visible scars.
Although hair transplantation is expensive, it provides long-term results. After the procedure, men often continue using treatments like finasteride or minoxidil to protect their remaining natural hair and maintain their new look.
How to Choose the Right Treatment Plan
Finding the best treatment for hereditary baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, depends on several factors. The goal is to choose an option that matches your needs, lifestyle, and stage of hair loss. By understanding your choices and working with a healthcare professional, you can take steps to manage hair loss effectively.
Factors to Consider
- Cost
The price of treatment is an important factor to think about. Medications like finasteride (Propecia) or minoxidil (Rogaine) are affordable for long-term use. On the other hand, advanced treatments like hair transplantation can be more expensive, often costing thousands of dollars. Decide on a budget and explore treatments that give you the best value for your money. - Severity of Hair Loss
The extent of your hair loss plays a big role in choosing a treatment. If you are in the early stages, with thinning hair or a receding hairline, medications like finasteride or minoxidil may work well. For more advanced baldness, measured using tools like the Norwood scale, surgical options such as follicular unit extraction (FUE) may be better for achieving noticeable results. - Personal Preference
Think about how each treatment fits into your daily routine and long-term goals. For example, finasteride is a pill taken once a day, while minoxidil needs to be applied to the scalp twice daily. If you prefer convenience, you might lean toward simpler options. Some people may avoid surgery, while others might see a hair transplant as a permanent solution they value.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Talking to a doctor or dermatologist is highly recommended when deciding on a treatment. A healthcare professional can assess your condition, determine the causes of your hair loss, and suggest treatments that suit your situation. They can also monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed to get the best results.
For many men, starting with medications like finasteride or minoxidil is a good first step. These treatments are well-researched and often form the foundation for managing hereditary baldness.
Creating Your Personalized Plan
Choosing a treatment plan is about finding a solution that works for you. Start by identifying your goals—whether you want to slow hair loss, encourage regrowth, or address more advanced baldness with surgery. Combine these goals with professional advice to create a plan that meets your needs and expectations.
Taking action early can help preserve your hair and boost your confidence. Wherever you are in your hair loss journey, making informed decisions will help you manage the condition effectively.
Living with Hair Loss
Hair loss is a natural and common experience that affects millions of men around the world. While some may see it as a major or permanent change, it’s important to understand that hair loss doesn’t determine your worth or confidence. By normalizing the experience and learning about available treatments, you can take control of your journey and find solutions that work for you.
Hair Loss Is a Shared Experience
By the age of 35, about 66% of men will experience some level of hair loss, and the chances increase with age. This shows that hair loss is not something unusual—it’s a reality many people face. Knowing this can help reduce the stigma of baldness and create a sense of connection among men going through similar challenges.
Hereditary baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, often follows predictable patterns caused by genetics. Understanding how and why it happens can make the process less overwhelming. Tools like the Norwood scale help track the extent of hair loss and guide you toward the best treatment options.
Why Early Action Matters
Taking steps early in your hair loss journey can improve the results of treatment. Medications like finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) work best when used in the early stages of baldness. These treatments can slow down hair loss, encourage regrowth, and help keep the hair you already have.
For those considering surgical options, such as hair transplantation, starting early can lead to better results. Acting sooner can reduce the amount of hair loss you experience and improve the effectiveness of both surgical and non-surgical solutions.
Confidence Beyond Hair
Hair is just one part of your appearance—it doesn’t define who you are. Many men feel more confident by embracing their hair loss, whether through shaving their heads, trying new hairstyles, or focusing on other aspects of self-care.
For others, knowing there are effective treatments available can provide reassurance. Whether it’s exploring medications like finasteride and minoxidil or considering advanced options like hair transplantation, the key is to choose what feels right for you. Confidence comes from understanding your options and taking control of your decisions.
Moving Forward with Hair Loss
Hair loss doesn’t have to be a defining moment—it’s a part of life that can be managed in different ways. By seeing it as a shared experience, exploring early treatments, and focusing on building confidence, you can take charge of your appearance and well-being. Modern treatments and a positive outlook can help you navigate this change with assurance and dignity.
Conclusion
Hereditary baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, is no longer something men have to face without solutions. Advances in modern treatments and a better understanding of hair loss have made it possible to manage and even reverse its effects. Whether your goal is to slow hair loss, encourage regrowth, or explore advanced procedures like hair transplantation, there are options available to suit different needs and stages of baldness.
A Reassuring Perspective
Hair loss can feel overwhelming, but it is a natural experience shared by many. About 66% of men experience some degree of hair loss by the age of 35. This shows that hair loss is not an isolated issue but something many people face.
Treatments like finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) have proven to be effective in slowing hair loss and, in some cases, even promoting regrowth. For those with more significant hair loss, advanced solutions such as hair transplantation offer long-term results. These options give men the opportunity to take control of their appearance and feel more confident.
Modern medicine has shifted the conversation about hereditary baldness from inevitability to opportunity. Today, men can manage hair loss in ways that align with their goals and preferences, allowing them to maintain or restore their confidence.
Taking the Next Step
The best way to address hereditary baldness is to take action. Many men start with medications like finasteride or minoxidil, which are well-researched and effective in managing hair loss. Speaking with a healthcare professional can help you determine the best treatment plan based on your level of hair loss and personal needs.
For those who want a more comprehensive approach, combining treatments or exploring surgical options like follicular unit extraction (FUE) can be effective. The key is understanding the available choices and finding what works best for you.
Don’t wait to address hair loss—starting early can make a big difference. Learn more about the wide range of hair loss medications available and explore the treatments that can help you achieve your goals. Visit our hair loss category page to discover options and take the first step toward managing hereditary baldness effectively.
FAQs About Hereditary Baldness
Hereditary baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, often raises questions for those experiencing hair loss. Learning more about the condition can help you make informed decisions about managing it. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about hereditary baldness, its causes, and available treatments.
What Causes Hereditary Baldness?
Hereditary baldness is caused by genetics. It often runs in families and can be passed down from either side of your family. The main factor behind this condition is a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is created from testosterone.
Some men are more sensitive to the effects of DHT, which causes hair follicles to shrink over time. This shrinkage weakens the hair, making it thinner and shorter until the follicles stop producing hair altogether. Hair loss patterns, such as thinning at the crown or receding hairlines, are often predictable and categorized using the Norwood scale, which helps measure the extent of baldness.
Are Treatments Like Finasteride and Minoxidil Safe?
Both finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) are well-studied treatments that are safe and effective for most men.
- Finasteride: This daily pill lowers DHT levels in the body, helping to slow hair loss and, in many cases, encourage hair regrowth. Most users tolerate it well, but some may experience mild side effects like reduced libido or dizziness. It’s a good idea to talk to a doctor before starting treatment.
- Minoxidil: This is a topical solution or foam applied to the scalp twice daily. It works by improving blood flow to the scalp, which helps stimulate hair growth in weakened follicles. Most users find it safe, but some may notice mild irritation or dryness on the scalp.
Both treatments are more effective when used as directed, and consulting a healthcare professional can help determine if they’re right for you.
How Much Does a Hair Transplant Cost?
The cost of a hair transplant depends on factors like how much hair loss you have, the technique used, and the clinic’s location.
- The most advanced method, called follicular unit extraction (FUE), involves transplanting individual hair follicles for natural-looking results.
- Costs typically range from $4,000 to $15,000, depending on how many grafts are needed.
While hair transplantation is expensive, it is often seen as a long-term investment because the transplanted hair is permanent. However, doctors often recommend continuing treatments like finasteride or minoxidil after the procedure to maintain the surrounding natural hair.
Can I Combine Treatments?
Yes, combining treatments is a common and effective way to manage hereditary baldness. For example:
- Using finasteride to lower DHT levels and minoxidil to improve blood flow can work well together.
- Adding ketoconazole shampoo to your routine can reduce DHT on the scalp and support overall hair health.
- After a hair transplant, continuing with medications like finasteride can help protect the remaining natural hair from further loss.
A combination approach allows you to address different causes of hair loss and maximize your results.
Information provided on this website is for general purposes only. It is not intended to take the place of advice from your practitioner