7 Signs That Point to Clinical Depression
|
Reading time: 9 minutes
|

Key Takeaways
- Clinical depression lasts for weeks or months and impacts emotions, energy levels, and brain function. It can also cause physical symptoms like chronic pain, fatigue, and changes in appetite.
- People with depression may experience persistent sadness, lack of motivation, trouble focusing, and sleep issues. Treatment options include therapy, lifestyle changes, and mental health medications, such as antidepressants, which help manage symptoms.
- Each person responds to treatment in their own way. Some improve with therapy alone, while others benefit from a mix of medication, counseling, and self-care. Speaking with a healthcare provider can help find the best plan for long-term well-being.
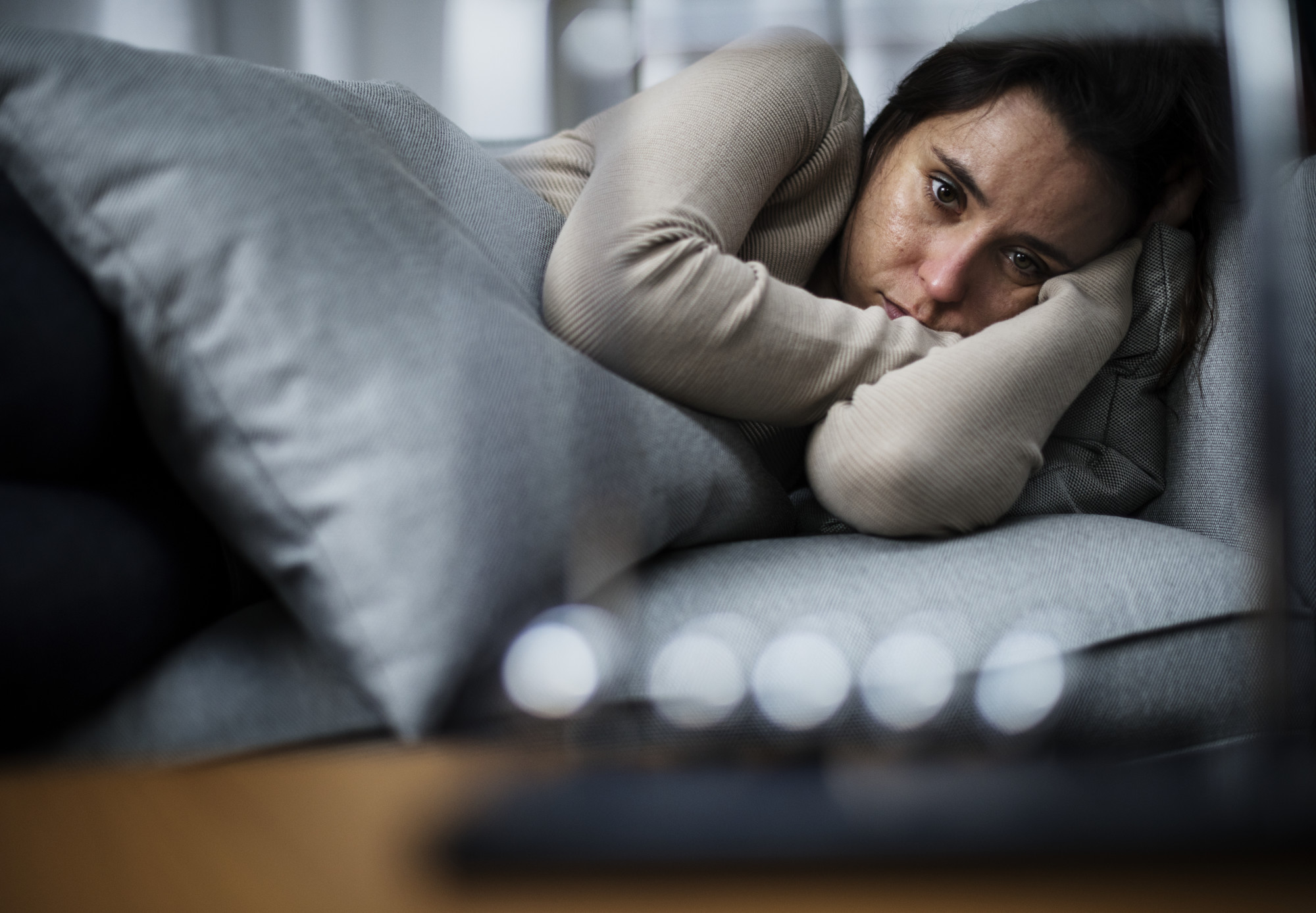
According to studies, roughly 8% of adults will experience clinical depression at some point in their lives. Clinical depression is a mental disorder that affects mood, thoughts, and daily life. It lasts for weeks or months, making it difficult to function as usual. It affects the way a person thinks, feels, and functions. Unlike temporary sadness caused by life challenges—such as losing a job or going through a breakup—clinical depression continues even when there is no clear reason for it.
This condition affects brain chemistry by disrupting neurotransmitters within the brain, making it difficult to feel happy, motivated, or emotionally balanced.” Many people with depression feel down most of the time, even when good things happen. The impact goes beyond emotions—it can cause problems with sleep, energy levels, and concentration. Some individuals find it hard to keep up with work, maintain relationships, or complete everyday tasks.
Depression can have many causes. It may be linked to family history, stressful experiences, long-term health conditions, or chemical imbalances in the brain. While some people see improvements through healthy habits and social support, others may need medical treatment.
Mental health medications, such as antidepressants, help regulate mood and support emotional stability. Many individuals benefit from a combination of therapy, self-care, and medication to manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Clinical Depression
Clinical depression affects both the mind and body, changing the way a person thinks, feels, and interacts with others. Unlike temporary sadness, which fades over time, depression lasts for weeks or months and can make everyday life more difficult. Recognizing the symptoms can help individuals understand when they may need support.
Depression does not look the same for everyone. Some people feel overwhelmed with sadness, while others lose motivation or experience extreme tiredness. The symptoms below often appear together, affecting emotions, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Common Symptoms of Clinical Depression
Persistent Low Mood – A person with depression may feel sad, empty, or hopeless most of the time. This emotional weight can make it difficult to enjoy activities or spend time with others.
Fatigue and Low Energy – Even with enough rest, individuals with depression often feel exhausted. Some sleep for long hours but still feel drained, while others struggle to get out of bed or complete daily tasks.
Difficulty Concentrating – Work, school, and daily decision-making can become challenging. Thoughts may feel foggy, and remembering details may take more effort.
Feelings of Guilt or Worthlessness – Some individuals experience strong feelings of self-blame or believe they are a burden to others. This can happen even when there is no clear reason for these emotions.
Changes in Appetite – Some people lose their appetite and experience weight loss, while others eat more than usual, leading to weight gain. These changes often happen without the person realizing it.
Loss of Interest – Activities, hobbies, or relationships that once brought joy may no longer feel enjoyable. Many individuals with depression withdraw from friends and family and prefer to be alone.
Suicidal Thoughts – Frequent thoughts about death, self-harm, or suicide are serious signs of depression. If these thoughts occur, speaking with a professional as soon as possible can provide support and treatment options.
When symptoms last for long periods, they can interfere with everyday life. Mental health professionals may recommend therapy, lifestyle changes, or mental health medications to help manage depression. Each person’s treatment plan is different, and early support can improve long-term well-being.
The Connection Between Depression and Physical Health
Depression affects more than emotions—it also impacts the body in ways that can lead to long-term health problems. Many people with depression experience physical symptoms, and those with ongoing health conditions may be more likely to develop depression. Mental and physical health are closely connected, and challenges in one area can affect the other.
How Depression Affects the Body
Depression changes the way the brain and body work together. It affects the nervous system, immune system, and overall energy levels. Some common physical effects of depression include:
- Chronic Pain – Depression can make aches, headaches, or muscle stiffness worse, even when there is no clear cause. Mood changes and stress can increase pain sensitivity.
- Digestive Problems – Some individuals with depression feel nauseous, experience stomach pain, or notice changes in appetite. This can lead to weight loss or weight gain.
- Low Energy Levels – Many people with depression feel physically drained, even after sleeping. Simple tasks may feel difficult or overwhelming.
- Sleep Disruptions – Some struggle to fall asleep, while others sleep too much. Irregular sleep patterns can worsen fatigue and affect overall health.
Depression and Chronic Illnesses
Depression often appears alongside long-term health conditions, especially when pain, fatigue, or medical challenges become difficult to manage. Some health conditions linked to depression include:
- Diabetes – Changes in blood sugar levels can impact mood, and managing diabetes daily can add emotional stress.
- Heart Disease – Depression can increase stress hormones, which may raise blood pressure and affect heart health.
- Autoimmune Disorders – Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus cause chronic inflammation, which can lead to depressive symptoms.
Can Depression Weaken the Immune System?
Mental health and immune function work together. People with depression may have a harder time fighting infections, healing from injuries, or managing inflammation. Stress hormones released during depression can weaken the body’s ability to stay healthy.
Managing Depression and Physical Health Together
Taking care of both mental and physical health can improve overall well-being. Doctors and mental health professionals may recommend:
- Therapy – Speaking with a professional can help individuals manage emotions and develop coping strategies.
- Lifestyle Changes – Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and good sleep habits can support both mental and physical health.
- Medication – Some individuals benefit from mental health medications, such as antidepressants, which help stabilize mood and reduce symptoms that interfere with daily life.
Recognizing how depression and physical health are connected allows individuals to seek treatment that addresses both. Managing symptoms early can help improve mood, energy levels, and overall health.
Effective Treatment Options for Clinical Depression
Clinical depression can be treated in different ways, depending on how it affects each person. Some people feel better with therapy, while others may need medication or lifestyle changes. In more serious cases, advanced treatments may be recommended. Finding the right treatment often takes time, and a combination of approaches may provide the best results.
A. Antidepressant Medications
Depression affects the brain’s chemical balance, which can lead to feelings of sadness, anxiety, or low motivation. Antidepressants help adjust these chemicals to support emotional well-being.
- Wellbutrin (Bupropion) is a medication that can help improve mood and boost energy levels.
- Some antidepressants increase serotonin, while others target dopamine or norepinephrine to improve focus and emotional stability.
- These medications often work better when combined with therapy or other mental health treatments.
B. Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy)
Talking to a therapist helps people understand their emotions and develop healthier ways to handle stress. Therapy can also teach new coping skills for daily life challenges.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify negative thinking patterns and replace them with more positive perspectives.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) focuses on improving relationships and communication skills to strengthen emotional connections.
- Many people see the best results when therapy is combined with mental health medications for both emotional and biological support.
C. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
For severe cases of depression that do not improve with medication or therapy, Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) may be considered. This treatment sends mild electrical signals to the brain to help reset certain pathways.
- ECT is done under medical supervision and used when other treatments are ineffective.
- Some individuals notice improvements after a few sessions, especially in cases of deep and persistent depression.
D. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment that stimulates brain activity linked to depression.
- A small device placed on the scalp sends magnetic pulses to activate nerve cells responsible for mood regulation.
- TMS is often used when antidepressants do not provide the expected results.
- This treatment does not require anesthesia and may be a better option for people who cannot take medication.
Finding the Right Treatment Plan
Depression affects each person differently, so treatment plans are often adjusted based on individual needs. Some people improve with therapy alone, while others may require mental health medications to manage symptoms. Speaking with a doctor or mental health professional can help determine the best approach for long-term recovery.
Seeking Help and Moving Forward
Dealing with depression can feel challenging, but help is available. Many people experience similar struggles, and reaching out for support can make a difference. Whether symptoms are mild or severe, finding the right treatment can improve emotional well-being and make daily life more manageable.
Building a Support System
Talking to others can provide comfort and reassurance. Friends, family members, and support groups can offer encouragement and help individuals feel less alone. Having strong emotional support can play a key role in recovery.
- Trusted conversations – Talking to someone who understands can reduce feelings of loneliness.
- Support groups – Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide a sense of community.
- Encouragement from loved ones – Family and friends can help make treatment and recovery feel more manageable.
Making Lifestyle Adjustments
Small changes in daily habits can help improve mood and overall well-being. While depression can make it difficult to stay motivated, gradual adjustments may support both mental and physical health.
- Staying active – Walking, stretching, or light exercise may help boost energy levels.
- Improving sleep habits – Creating a regular sleep routine can support emotional balance and reduce fatigue.
- Eating nutritious foods – A balanced diet provides the brain with essential nutrients that support mental health.
Exploring Treatment Options
Some individuals find that professional treatment helps them manage depression more effectively. Therapy, medication, or a combination of both may provide long-term support.
- Speaking with mental health professionals – Therapists, counselors, or doctors can assess symptoms and suggest the best treatment plan.
- Trying psychotherapy – Talking with a therapist can help individuals understand their emotions and learn better ways to cope.
- Considering mental health medications – Some people benefit from antidepressants, which help regulate mood and brain function.
Accessing Medication and Support
For those exploring medication as part of their treatment, consulting a healthcare provider can provide helpful guidance. Many individuals find relief through prescription antidepressants, which are often used alongside therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
Online Pharmacies Canada offers a range of mental health medications, including prescription antidepressants and alternative options for managing depression. If you have questions about available treatments, our team is here to help.
Information provided on this website is for general purposes only. It is not intended to take the place of advice from your practitioner